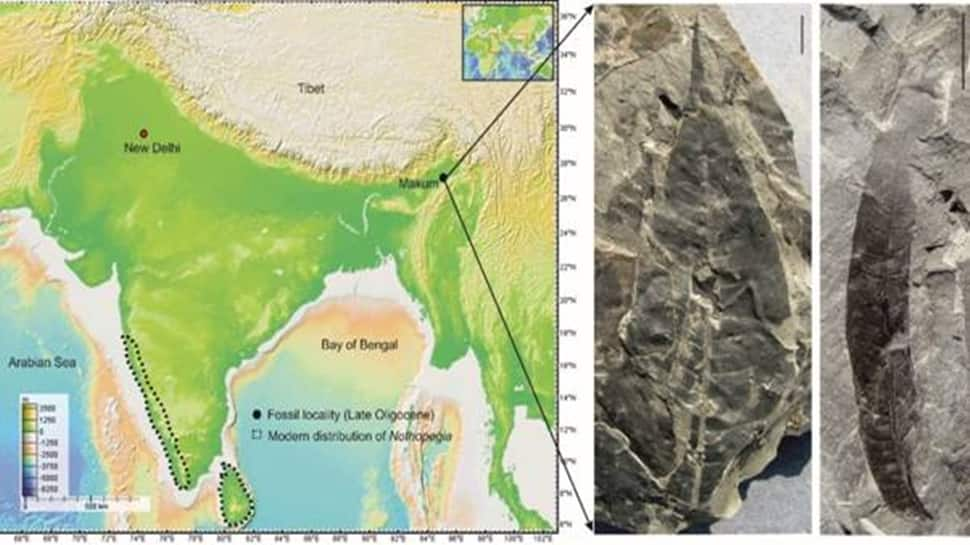
Ancient Scientific Discovery In India: Scientists exploring ancient coal deposits in northeast India have made a significant discovery: fossilized leaves that are challenging long-held beliefs about South Asia’s biodiversity. The research began after fossil leaves, recognized by some scientists, were found in Assam’s Makum Coalfield, an area rich in fossil discoveries, said the Ministry of Science in a statement. A team from the Birbal Sahni Institute of Palaeosciences (BSIP), an autonomous institute under the Department of Science and Technology (DST), collected these fossil leaves. They meticulously analyzed their physical characteristics and identified them through comparisons with existing plant collections and cluster analysis, said the ministry.
Their findings revealed a striking resemblance to modern plant species of the Nothopegia genus. What makes this particularly noteworthy is that Nothopegia plants currently thrive thousands of kilometers away in the rain-soaked forests of the Western Ghats, a UNESCO World Heritage Site and a global biodiversity hotspot. This discovery suggests a much broader historical distribution for these plants than previously understood.
“These fossilized leaves, dating back around 24–23 million years to the late Oligocene epoch, were the world’s oldest known fossil record of a plant genus called Nothopegia. Strangely, the genus is not found in northeast India anymore. The scientists traced the journey of the species from the Northeast of the subcontinent to the Western Ghats in the study published in the journal Review of Palaeobotany and Palynology,” it said.
Back in the late Oligocene, the climate of Northeast India was very different. Using advanced techniques like the Climate Leaf Analysis Multivariate Program (CLAMP), scientists reconstructed a warm, humid climate — much like what the Western Ghats experience today.
This suggested that the ancient environment of northeast India once provided a perfect home for Nothopegia. But over millions of years, monumental forces reshaped the landscape. The Himalayas began their dramatic rise due to tectonic movements, bringing with them sweeping changes in temperature, rainfall, and wind patterns. These geological convulsions cooled the northeast, rendering it inhospitable for many tropical plant species, including Nothopegia, which vanished from the region. Yet, the species survived in the climatically stable Western Ghats, making it a living relic of an ancient ecological past.
The tracing of the changes was possible through a combination of paleobotany, systematics, and climate modelling — a powerful multidisciplinary approach that lets us peer millions of years into the past. But this is more than a tale of disappearing leaves — it’s a glimpse into how ecosystems evolve under pressure and how some lineages survive dramatic environmental shifts.
The study shows that extinction and migration driven by climate change is not new — they’ve been shaping our planet’s biodiversity for eons. But unlike ancient climate shifts, today’s changes are happening at an unprecedented pace, driven by human activity.
Understanding how Nothopegia once migrated and found refuge helps scientists predict how modern plants might respond to global warming. It also highlights the importance of protecting biodiversity refuges like the Western Ghats, where ancient lineages continue to persist against the odds.
As co-author Dr. Harshita Bhatia puts it, “This fossil discovery is a window into the past that helps us understand the future.” Her team’s work adds a critical piece to the puzzle of how India’s rich biodiversity can be saved from the climatic challenges ahead.